Streamline Security with https//bit.ly/workforce-sso
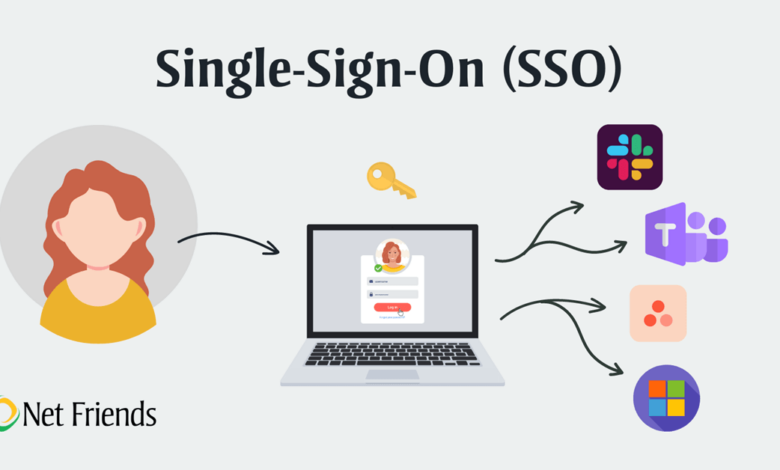
What is Single Sign-On (SSO)?
Single Sign-On is an authentication process that enables users to access multiple applications with one set of login credentials. Imagine a scenario where you only need to remember one password instead of several. Wouldn’t that simplify your daily routine? With SSO, users log in once and can seamlessly navigate through various applications without the hassle of repeated logins.
The Benefits of SSO
- Enhanced Security: One of the most significant advantages of SSO is improved security. By reducing the number of passwords users need to remember, organizations can mitigate the risk of weak or reused passwords, which are often exploited by cybercriminals. Did you know that a staggering 81% of data breaches are linked to compromised credentials? Implementing SSO can help safeguard sensitive information by centralizing authentication and reducing exposure to potential attacks source.
- Improved User Experience: How often do you find yourself frustrated by forgotten passwords? SSO eliminates this issue by allowing users to access all necessary applications with a single login. This not only enhances productivity but also boosts user satisfaction as employees can focus more on their work rather than on password management source.
- Streamlined Access Management: For IT departments, managing user access becomes significantly easier with SSO. Administrators can control access from a central point, making it simpler to add or remove users and manage permissions across various platforms. This centralized approach not only saves time but also ensures compliance with security policies source.
- Cost Efficiency: While there may be initial costs associated with implementing SSO solutions, the long-term savings in terms of reduced help desk calls for password resets and improved productivity often outweigh these expenses source. Organizations can allocate resources more effectively when employees spend less time dealing with login issues.
Implementing SSO in Your Organization
Choosing an Identity Provider (IdP)
To implement SSO, organizations typically partner with an Identity Provider (IdP) that manages user identities and authentication processes. Popular IdPs include Azure Active Directory, Okta, and G Suite. When selecting an IdP, consider factors such as compatibility with existing systems, ease of integration, and support for various authentication protocols like SAML 2.0 source.
Configuration Steps
Setting up SSO involves several key steps:
- Configure Your IdP: Begin by setting up your IdP according to your organization’s requirements. This includes defining user roles and permissions.
- Integrate with Applications: Next, integrate your IdP with the applications your workforce uses daily. Ensure that each application supports SAML or OpenID Connect protocols for seamless integration source.
- Test the Setup: Before rolling out SSO organization-wide, conduct thorough testing to ensure that the authentication process works smoothly across all integrated applications.
- Educate Your Workforce: Once implemented, provide training sessions for employees to familiarize them with the new login process. Clear communication will help alleviate any concerns regarding the transition source.
Best Practices for SSO Implementation
- Use Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): While SSO enhances security, combining it with MFA adds another layer of protection. MFA requires users to provide additional verification methods—such as a text message code or biometric recognition—making unauthorized access even more difficult source.
- Regularly Review Access Permissions: Periodically audit user access rights to ensure that only authorized individuals have access to sensitive data and applications source.
- Monitor User Activity: Implement monitoring tools that track user activity within applications accessed through SSO. This can help identify unusual behavior that may indicate security breaches source.
- Stay Updated on Security Protocols: Technology evolves rapidly; staying informed about the latest security threats and updates in authentication protocols is crucial for maintaining a secure environment source.
Conclusion
Adopting Single Sign-On is not just about convenience; it’s a strategic move towards enhancing security and improving operational efficiency within organizations. By streamlining user access while safeguarding sensitive information, SSO empowers both employees and IT departments alike.
Have you considered how implementing SSO could benefit your organization? The transition may seem daunting at first, but the long-term advantages far outweigh any initial challenges. As you explore this option, remember that investing in robust identity management solutions today can pave the way for a more secure and efficient future for your workforce.
By embracing technologies like Single Sign-On, organizations can create a more productive work environment while fortifying their defenses against cyber threats—because in today’s digital landscape, security should never be an afterthought!
Read More:




